”Question: What types of exercise are possible with limited mobility?
Reading time: 12 Minutes
MWi Hacks:
- Learn different ways to exercise with limited mobility
- Understand how to get started with an exercise routine
MWi Summary:
- Exercise has many physical, mental, and emotional benefits even if you have limited mobility due to disability, injury, or chronic disease.
- Talk to your health care provider about activities that are suitable for your ability. You should ask questions on how often you should exercise and if there are certain activities you should avoid.
- Consistency is one of the most important factors in starting and sticking with an exercise routine. Also, celebrate your effort when you make the time to exercise.
- Some tips on staying safe when exercising are stopping if you experience pain, warm up and cool down properly, and drink plenty of water.
- There are many different cardiovascular and strength exercises that can be done from a wheelchair such as chair aerobics and dumbbell exercises.
- If you are overweight or have diabetes, a helpful place to start with exercise is finding ways to incorporate physical activity into your daily life, like walking.
Don’t let injury, disability, illness, or weight problems get in the way. These chair exercises and other simple fitness tips can keep you active and improve your health and well-being.
Limited mobility doesn’t mean you can’t exercise
You don’t need to have full mobility to experience the health benefits of exercise. If injury, disability, illness, or weight problems have limited your mobility, there are still plenty of ways you can use exercise to boost your mood, ease depression, relieve stress and anxiety, enhance your self-esteem, and improve your whole outlook on life.
When you exercise, your body releases endorphins that energize your mood, relieve stress, boost your self-esteem, and trigger an overall sense of well-being. If you’re a regular exerciser currently sidelined with an injury, you’ve probably noticed how inactivity has caused your mood and energy levels to sink. This is understandable: exercise has such a powerful effect on mood that it can treat mild to moderate depression as effectively as antidepressant medication. However, an injury doesn’t mean your mental and emotional health is doomed to decline. While some injuries respond best to total rest, most simply require you to reevaluate your exercise routine with help from your doctor or physical therapist.
If you have a disability, severe weight problem, chronic breathing condition, diabetes, arthritis, or other ongoing illness, you may think that your health problems make it impossible for you to exercise effectively, if at all. Or perhaps you’ve become frail with age and are worried about falling or injuring yourself if you try to exercise. The truth is, regardless of your age, current physical condition, and whether you’ve exercised in the past or not, there are plenty of ways to overcome your mobility issues and reap the physical, mental, and emotional rewards of exercise.
What types of exercise are possible with limited mobility?
It’s important to remember that any type of exercise will offer health benefits. Mobility issues inevitably make some types of exercise easier than others, but no matter your physical situation, you should aim to incorporate three different types of exercise into your routines:
Cardiovascular exercises raise your heart rate and increase your endurance. These can include walking, running, cycling, dancing, tennis, swimming, water aerobics, or “aquajogging”. Many people with mobility issues find exercising in water especially beneficial as it supports the body and reduces the risk of muscle or joint discomfort. Even if you’re confined to a chair or wheelchair, it’s still possible to perform cardiovascular exercise.
Strength training exercises involve using weights or other resistance to build muscle and bone mass, improve balance, and prevent falls. If you have limited mobility in your legs, your focus will be on upper body strength training. Similarly, if you have a shoulder injury, for example, your focus will be more on strength training your legs and core.
Flexibility exercises help enhance your range of motion, prevent injury, and reduce pain and stiffness. These may include stretching exercises and yoga. Even if you have limited mobility in your legs, for example, you may still benefit from stretches and flexibility exercises to prevent or delay further muscle atrophy.
Setting yourself up for exercise success
To exercise successfully with limited mobility, illness, or weight problems, start by getting medical clearance. Talk to your doctor, physical therapist, or other health care provider about activities suitable for your medical condition or mobility issue.
Talking to your doctor about exercise
Your doctor or physical therapist can help you find a suitable exercise routine. Ask:
- How much exercise can I do each day and each week?
- What type of exercise should I do?
- What exercises or activities should I avoid?
- Should I take medication at a certain time around my exercise routine?
Starting an exercise routine
Start slow and gradually increase your activity level. Start with an activity you enjoy, go at your own pace, and keep your goals manageable. Accomplishing even the smallest fitness goals will help you gain body confidence and keep you motivated.
Make exercise part of your daily life. Plan to exercise at the same time every day and combine a variety of exercises to keep you from getting bored.
Stick with it. It takes about a month for a new activity to become a habit. Write down your reasons for exercising and a list of goals and post them somewhere visible to keep you motivated. Focus on short-term goals, such as improving your mood and reducing stress, rather than goals such as weight loss, which can take longer to achieve. It’s easier to stay motivated if you enjoy what you’re doing, so find ways to make exercise fun. Listen to music or watch a TV show while you work out, or exercise with friends.
Expect ups and downs. Don’t be discouraged if you skip a few days or even a few weeks. It happens. Just get started again and slowly build up to your old momentum.
Staying safe when exercising
Stop exercising if you experience pain, discomfort, nausea, dizziness, lightheadedness, chest pain, irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, or clammy hands. Listening to your body is the best way to avoid injury. If you continually experience pain after 15 minutes of exercise, for example, limit your workouts to 5 or 10 minutes and instead exercise more frequently.
Avoid activity involving an injured body part. If you have an upper-body injury, exercise your lower body while the injury heals, and vice versa. When exercising after an injury has healed, start back slowly, using lighter weights and less resistance.
Warm-up, stretch and cool down. Warm-up with a few minutes of light activity such as walking, arm swinging, and shoulder rolls, followed by some light stretching (avoid deep stretches when your muscles are cold). After your exercise routine, whether it’s cardiovascular, strength training, or flexibility exercise, cool down with a few more minutes of light activity and deeper stretching.
Drink plenty of water. Your body performs best when it’s properly hydrated.
Wear appropriate clothing, such as supportive footwear and comfortable clothes that won’t restrict your movement.
Getting more out of your workouts
Add a mindfulness element. Whether you’re exercising in a chair or walking outside, you’ll experience a greater benefit if you pay attention to your body instead of zoning out. By really focusing on how your body feels as you exercise—the rhythm of your breathing, your feet striking the ground, your muscles tightening as you lift weights, for example—you’ll not only improve your physical condition faster, but may also experience greater benefits to your mood and sense of well-being.
Overcoming mental and emotional barriers to exercise
As well as the physical challenges you face, you may also experience mental or emotional barriers to exercising. It’s common for people to feel self-conscious about their weight, disability, illness, or injury, and want to avoid working out in public places. Some older people find that they’re fearful about falling or otherwise injuring themselves.
Don’t focus on your mobility or health issue. Instead of worrying about the activities, you can’t enjoy, concentrate on finding activities that you can.
The more physical challenges you face, the more creative you’ll need to be to find an exercise routine that works for you. If you used to enjoy jogging or cycling, for example, but injury, disability, or illness means that they’re no longer options, be prepared to try new exercises. With some experimenting, it’s very possible that you’ll find something you enjoy just as much.
Be proud when you make the effort to exercise, even if it’s not very successful at first. It will get easier the more you practice.
| Barrier to exercise | Suggestion |
| I’m self-conscious about my weight, injury, or disability. | Exercise doesn’t have to mean working out in a crowded gym. You can try exercising early in the morning to avoid the crowds or skip the gym altogether. If you can afford it, a personal trainer will come to your home or work out with you at a private studio. Walking, swimming, or exercising in a class with others who have similar physical limitations can make you feel less self-conscious. There are also plenty of inexpensive ways to exercise privately at home. |
| I’m scared of injury. | Choose low-risk activities, such as walking or chair-bound exercises, and warm-up and cool-down correctly to avoid muscle strains and other injuries. |
| I can’t motivate myself. | Explain your exercise goals to friends and family and ask them to support and encourage you. Better still, find a friend to exercise with. You can motivate each other and turn your workouts into a social event. |
| I’m not coordinated or athletic. | Choose exercise that requires little or no skill, such as walking, cycling on a stationary bike, or aqua jogging (running in a swimming pool). |
| Exercise is boring. | But video games are fun. If traditional exercise is not for you, try playing activity-based video games, known as “exergames.” Games that simulate bowling, tennis, or boxing, for example, can all be played seated in a chair or wheelchair and are fun ways to burn calories and elevate your heart rate, either alone or playing along with friends. |
How to exercise with an injury or disability
Since people with disabilities or long-term injuries have a tendency to live less active lifestyles, it can be even more important for you to exercise on a regular basis.
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, adults with disabilities should aim for:
- At least 150 minutes a week of moderate-intensity, or 75 minutes a week of vigorous-intensity cardiovascular activity (or a combination of both), with each workout lasting for at least 10 minutes.
- Two or more sessions a week of moderate- or high-intensity strength-training activities involving all the major muscle groups.
If your disability or injury makes it impossible for you to meet these guidelines, aim to engage in regular physical activity according to your ability, and avoid inactivity whenever possible.
Workouts for upper-body injury or disability
Depending on the location and nature of your injury or disability, you may still be able to walk, jog, use an elliptical machine, or even swim using flotation aids. If not, try using a stationary upright or recumbent bike for cardiovascular exercise.
When it comes to strength training, your injury or disability may limit your use of free weights and resistance bands, or may just mean you have to reduce the weight or level of resistance. Consult with your doctor or physical therapist for safe ways to work around the injury or disability, and make use of exercise machines in a gym or health club, especially those that focus on the lower body.
Isometric exercises
If you experience joint problems from arthritis or an injury, for example, a doctor or physical therapist may recommend isometric exercises to help you maintain muscle strength or prevent further muscle deterioration. Isometric exercises require you to push against immovable objects or another body part without changing the muscle length or moving the joint.
Electro muscle stimulation
If you’ve experienced muscle loss from an injury, disability, or a long period of immobility, electro muscle stimulation may be used to increase blood circulation and range of motion in a muscle. Muscles are gently contracted with an electrical current transmitted via electrodes placed on the skin.
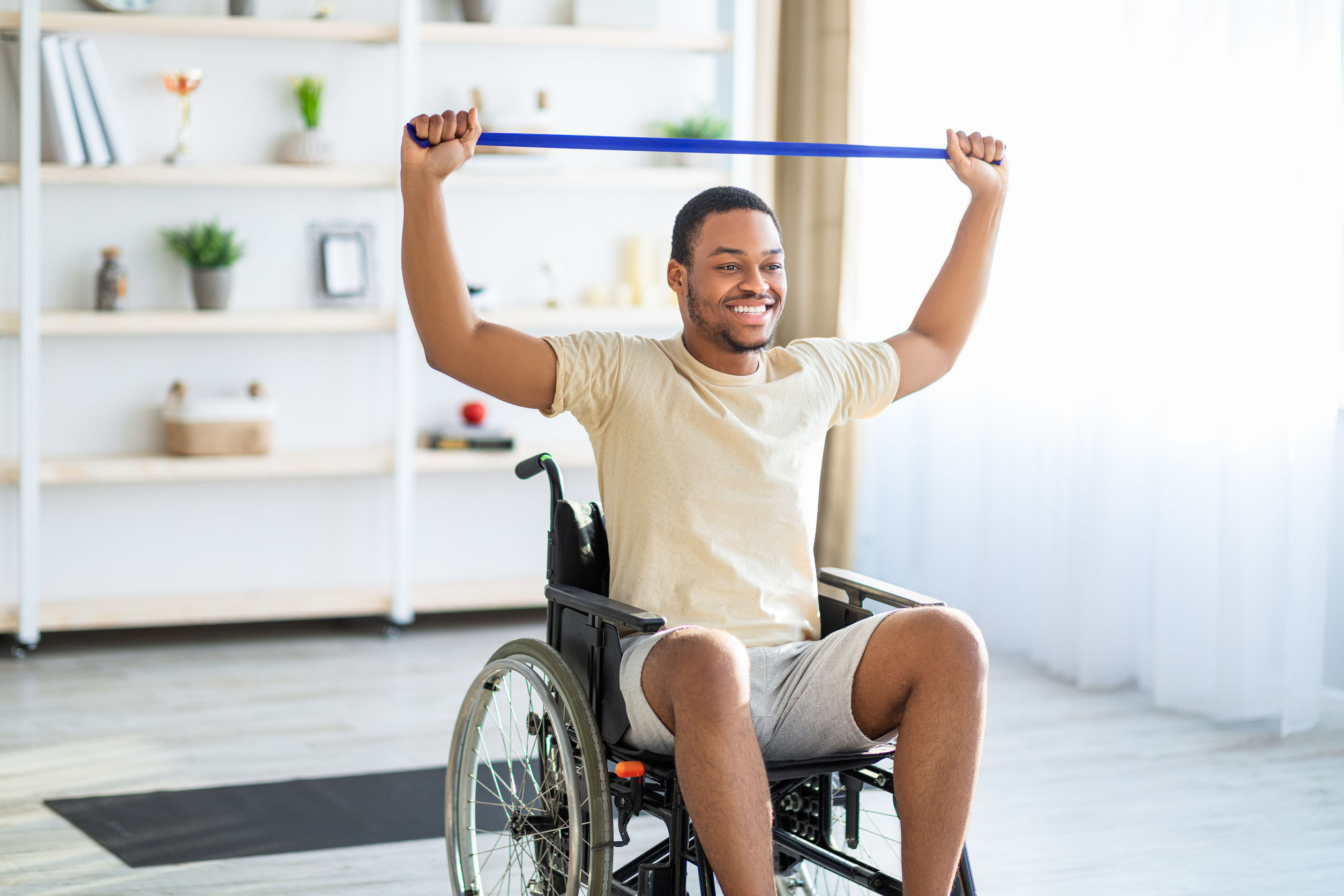
How to exercise in a chair or wheelchair
Chair-bound exercises are ideal for people with lower-body injuries or disabilities, those with weight problems or diabetes, and frail seniors looking to reduce their risk of falling. Cardiovascular and flexibility chair exercises can help improve posture and reduce back pain, while any chair exercise can help alleviate body sores caused by sitting in the same position for long periods. They’re also a great way to squeeze in a workout while you’re watching TV.
- If possible, choose a chair that allows you to keep your knees at 90 degrees when seated. If you’re in a wheelchair, securely apply the brakes or otherwise immobilize the chair.
- Try to sit up tall while exercising and use your abs to maintain good posture.
- If you suffer from high blood pressure, check your blood pressure before exercising and avoid chair exercises that involve weights.
- Test your blood sugar before and after exercise if you take diabetes medication that can cause hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Cardiovascular exercise in a chair or wheelchair
Chair aerobics, a series of seated repetitive movements, will raise your heart rate and help you burn calories, as will many strength training exercises when performed at a fast pace with a high number of repetitions. In fact, any rapid, repetitive movements offer aerobic benefits and can also help loosen stiff joints.
- Wrap a lightweight resistance band under your chair (or bed or couch, even) and perform rapid resistance exercises, such as chest presses, for a count of one second up and two seconds down. Try several different exercises to start, with 20 to 30 reps per exercise, and gradually increase the number of exercises, reps, and total workout time as your endurance improves.
- Simple air-punching, with or without hand weights, is an easy cardio exercise from a seated position and can be fun when playing along with a Nintendo Wii or Xbox 360 video game.
- Many swimming pools and health clubs offer pool-therapy programs with access for wheelchair users. If you have some leg function, try a water aerobics class.
- Some gyms offer wheelchair-training machines that make arm-bicycling and rowing possible. For a similar exercise at home, some portable pedal machines can be used with your hands when secured to a table in front of you.
Wheelchair sports
If you want to add competition to your workouts, several organizations offer adaptive exercise programs and competitions for sports such as basketball, track and field, volleyball, and weightlifting.
Strength training
Many traditional upper body exercises can be executed from a seated position using dumbbells, resistance bands, or anything that is weighted and fits in your hand, like soup cans.
- Perform exercises such as shoulder presses, bicep curls, and tricep extensions using heavier weights and more resistance than you would for cardio exercises. Aim for two to three sets of 8 to 12 repetitions for each exercise, adding weight and more exercises as your strength improves.
- Resistance bands can be attached to furniture, a doorknob, or your chair. Use these for pull-downs, shoulder rotations, and arm and leg extensions.
Flexibility exercise
If you’re in a wheelchair or have limited mobility in your legs, stretching throughout the day can help reduce pain and pressure on your muscles that often accompanies sitting for long periods. Stretching while lying down or practicing yoga or tai chi in a chair can also help increase flexibility and improve your range of motion.
To ensure yoga or tai chi is practiced correctly, it’s best to learn by attending group classes, hiring a private teacher, or at least following video instructions online.
Chair yoga and tai chi
Most yoga poses can be modified or adapted depending on your physical mobility, weight, age, medical condition, and any injury or disability. Chair yoga is ideal if you have a disability, injury, or a medical condition such as arthritis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoporosis, or multiple sclerosis. Similarly, seated versions of tai chi exercises can also be practiced in a chair or a wheelchair to improve flexibility, strength, and relaxation.
How to exercise if you’re overweight or have diabetes
Exercise can play a vital role in reducing weight and managing type 2 diabetes. It can stabilize blood sugar levels, increase insulin sensitivity, lower blood pressure, and slow the progression of neuropathy. But it can be daunting to start an exercise routine if you’re severely overweight. Your size can make it harder to bend or move correctly, and even if you feel comfortable exercising in a gym, you may have difficulty finding suitable equipment. When choosing a gym, make sure it offers exercise machines and weight benches that can support larger people.
Whatever your size, there are plenty of alternatives to health clubs. A good first step to exercising is to incorporate more activity into your everyday life. Gardening, walking to the store, washing the car, sweeping the patio, or pacing while talking on the phone are all easy ways to get moving. Even small activities can add up over the course of a day, especially when you combine them with short periods of scheduled exercise as well.
Cardiovascular workouts
- Weight-bearing activities such as walking, dancing, and climbing stairs use your own body weight as resistance. Start with just a few minutes a day and gradually increase your workout times. Make activities more enjoyable by walking with a dog, dancing with a friend, or climbing stairs to your favorite music.
- If you experience pain in your feet or joints when you stand, try non-weight-bearing activities. Water-based activities such as swimming, aqua jogging, or water aerobics place less stress on your feet and joints. Look for special classes at your local health club, YMCA, or swim center where you can exercise with other larger people. Other non-weight-bearing activities include chair exercises (see above).
- A portable pedal exerciser is a simple device that you can use while sitting in any comfortable chair at home while you watch TV—or even under your desk at work.
Strength training
- Many larger people find that using an exercise ball is more comfortable than a weight bench. Or you can perform simple strength training exercises in a chair.
- If you opt to invest in home exercise equipment, check the weight guidelines, and if possible, try the equipment out first to make sure it’s a comfortable fit.
- While strength training at home, it’s important to ensure that you’re maintaining good posture and performing each exercise correctly. Schedule a session with a personal trainer or ask a knowledgeable friend or relative to check your form.
Flexibility workouts
- Gentle yoga or tai chi are great ways to improve flexibility and posture, as well as reduce stress and anxiety.
https://www.helpguide.org/articles/healthy-living/chair-exercises-and-limited-mobility-fitness.htm